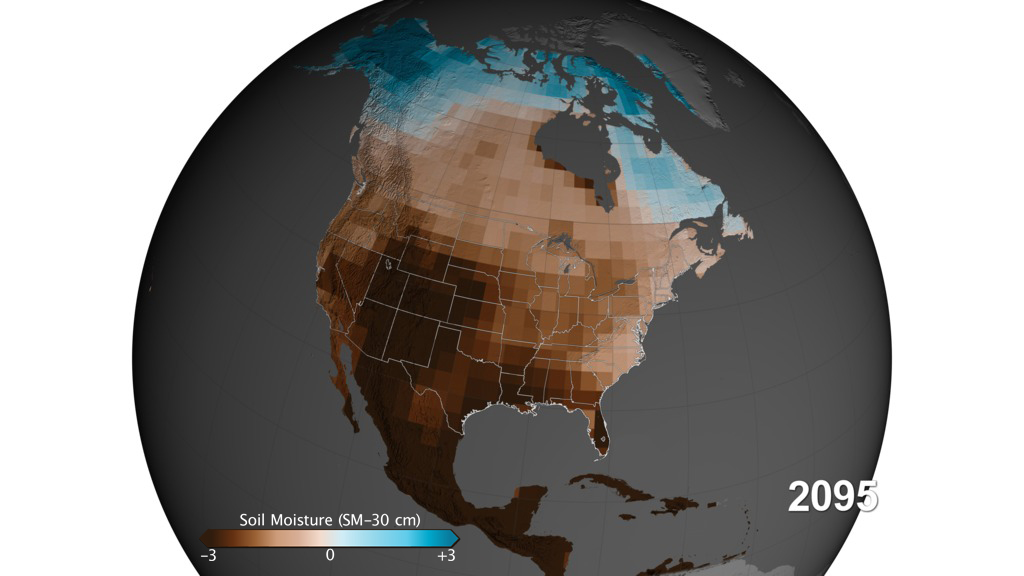
The long and severe drought in the U.S. Southwest pales in comparison with what’s coming: a “megadrought” that will grip that region and the central Plains later this century and probably stay there for decades, a new study says.
Thirty-five years from now, if the current pace of climate change continues unabated, those areas of the country will experience a weather shift that will linger for as long as three decades, according to the study, released Thursday.
Researchers from NASA and Cornell and Columbia universities warned of major water shortages and conditions that dry out vegetation, which can lead to monster wildfires in southern Arizona and parts of California.
“We really need to start thinking in longer-term horizons about how we’re going to manage it,” said Toby R. Ault, an assistant professor in the department of Earth and atmospheric sciences at Cornell, one of the co-authors. “This is a slow-moving natural hazard that humans are used to dealing with and used to managing.”
Megadroughts are sustained periods of sparse precipitation and significant loss of soil moisture that span generations, about 10 times as long as a normal three-year drought.
Tucson had less than 80 percent of its normal rainfall for long stretches in the 1990s. If that were to last for two decades, “that’s a megadrought,” Ault said.
Based on climate models the researchers used for the study, there is an 80 percent chance that such an extended drought will strike between 2050 and 2099, unless world governments act aggressively to mitigate impacts from climate change, the researchers said.
North America’s last megadroughts happened in medieval times, during the 12th and 13th centuries. They were caused by natural changes in weather that give megadroughts a 10 percent chance of forming at any time.
But climate change driven by human activity dramatically increases those chances. “With climate change, the likelihood of a megadrought goes up considerably,” Ault said.
The other writers for the study were its lead author, Benjamin I. Cook, a research scientist for NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies, and co-author Jason E. Smerdon, a research professor at Columbia’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory. The report was published Thursday in the journal Science Advances.
“We got some exciting, thrilling and important research,” said Marcia Kemper McNutt, a geophysicist and editor in chief of the journal Science. “We are facing a water situation that hasn’t been seen in California for 1,200 years.”
At the study’s presentation, Ault had a word of caution. Weather conditions can vary, climate impacts can be mitigated, and the warnings of the study might not come to pass. A single El Niño weather pattern in the West could interrupt periods of prolonged drought.
Smerdon said the researchers went back over a thousand years’ worth of data to look at conditions that caused drought in North America and observing patterns in tree rings to determine wet and dry periods.
After 2050, there is “overwhelming evidence of a dry shift,” he said, “way drier than the megadroughts of the 1100s and 1200s.” The cause, Smerdon continued, “is twofold, reductions in rainfall and snowfall. Not just rainfall but soil moisture . . . and changes in evaporation that dry out the soil much more than normal.”
The research is newly published, but its findings are not dramatically different from similar studies in the past. Beverly Law, a specialist in global change biology at Oregon State University’s College of Forestry, co-authored a study of megadroughts three years ago.
It showed that a drought that affected the American West from 2000 to 2004 compared to conditions seen during the medieval megadroughts. But the predicted megadrought this century would be far worse. Law said Thursday’s study confirmed her previous findings.
“We took the climate model . . . and compared” two periods, 2050 to 2099 and 1950 to 1999, she said. “What it showed is this big, red blotch over Southern California. It will really impact megacities, populations and water availability.”
Law is also co-author of an upcoming study commissioned by the U.S. Geological Survey about forest mortality later this century, and the preliminary findings are disturbing, she said.
According to predictions, the amount of precipitation in Arizona will be half of what it was between 1950 and 1999.
“We have drinking water to be concerned about,” she said. “That area’s really vulnerable.”
3 WAYS TO SHOW YOUR SUPPORT
- Log in to post comments